Image security insights
Strengthen the security of your Docker images with Docker Hub's image security insights. Docker Hub lets you perform either point-in-time static vulnerability scanning or always up-to-date image analysis using Docker Scout.
Docker Scout image analysis
After turning on Docker Scout image analysis, Docker Scout automatically analyzes images in your Docker Hub repository.
Image analysis extracts the Software Bill of Material (SBOM) and other image metadata, and evaluates it against vulnerability data from security advisories.
The following sections describe how to turn on or off Docker Scout image analysis for a Docker Hub repository. For more details about the image analysis, see Docker Scout.
Turn on Docker Scout image analysis
Sign in to Docker Hub.
Select My Hub > Repositories.
A list of your repositories appears.
Select a repository.
The General page for the repository appears.
Select the Settings tab.
Under Image security insight settings, select Docker Scout image analysis.
Select Save.
Turn off Docker Scout image analysis
Sign in to Docker Hub.
Select My Hub > Repositories.
A list of your repositories appears.
Select a repository.
The General page for the repository appears.
Select the Settings tab.
Under Image security insight settings, select None.
Select Save.
Static vulnerability scanning
メモDocker Hub static vulnerability scanning requires a Docker Pro, Team, or Business subscription.
When you push an image to a Docker Hub repository after turning on static scanning, Docker Hub automatically scans the image to identify vulnerabilities. The scan results shows the security state of your images at the time when the scan was run.
Scan results include:
- The source of the vulnerability, such as Operating System (OS) packages and libraries
- The version in which it was introduced
- A recommended fixed version, if available, to remediate the vulnerabilities discovered.
Changes to static scanning in Docker Hub
From February 27th, 2023, Docker changed the technology that supports the Docker Hub static scanning feature. The static scanning is now powered natively by Docker, instead of a third-party.
As a result of this change, scanning now detects vulnerabilities at a more granular level than before. This in turn means that vulnerability reports may show a higher number of vulnerabilities. If you used vulnerability scanning before February 27th, 2023, you may see that new vulnerability reports list a higher number of vulnerabilities, due to a more thorough analysis.
There is no action required on your part. Scans continue to run as usual with no interruption or changes to pricing. Historical data continues to be available.
Turn on static vulnerability scanning
Repository owners and administrators can enable static vulnerability scanning on a repository. If you are a member of a Team or a Business subscription, ensure the repository you would like to enable scanning on is part of the Team or a Business tier.
When scanning is active on a repository, anyone with push access can trigger a scan by pushing an image to Docker Hub.
To enable static vulnerability scanning:
メモStatic vulnerability scanning supports scanning images which are of AMD64 architecture, Linux OS, and are less than 10 GB in size.
Sign in to Docker Hub.
Select My Hub > Repositories.
A list of your repositories appears.
Select a repository.
The General page for the repository appears.
Select the Settings tab.
Under Image security insight settings, select Static scanning.
Select Save.
Scan an image
To scan an image for vulnerabilities, push the image to Docker Hub, to the repository for which you have turned on scanning.
View the vulnerability report
To view the vulnerability report:
Sign in to Docker Hub.
Select My Hub > Repositories.
A list of your repositories appears.
Select a repository.
The General page for the repository appears. It may take a couple of minutes for the vulnerability report to appear in your repository.
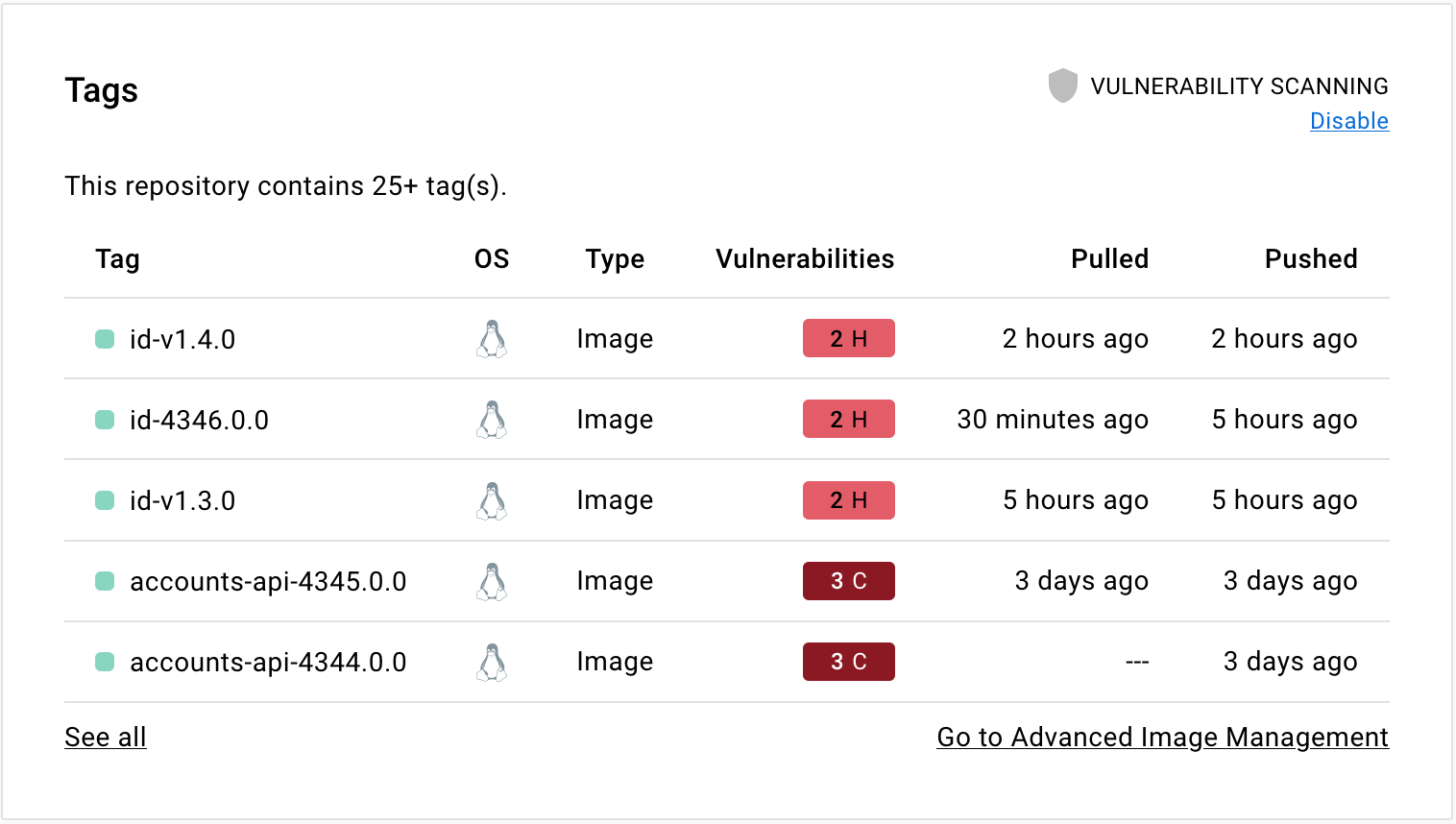

Select the Tags tab, then Digest, then Vulnerabilities to view the detailed scan report.
The scan report displays vulnerabilities identified by the scan, sorting them according to their severity, with highest severity listed at the top. It displays information about the package that contains the vulnerability, the version in which it was introduced, and whether the vulnerability is fixed in a later version.
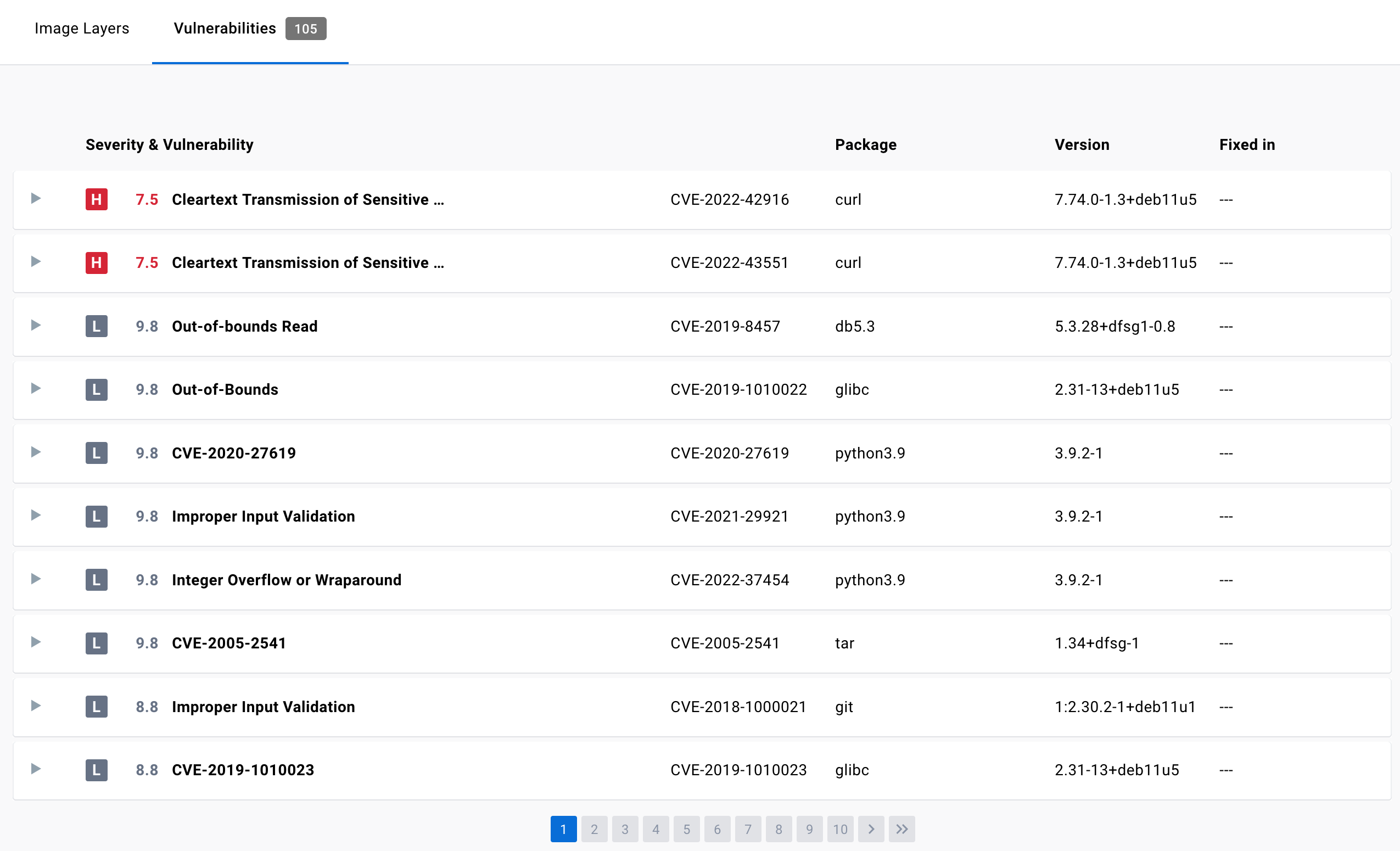

For more information on this view, see Image details view.
Inspect vulnerabilities
The vulnerability report sorts vulnerabilities based on their severity. It displays information about the package that contains the vulnerability, the version in which it was introduced, and whether the vulnerability has been fixed in a later version.
The vulnerability scan report also allows development teams and security leads to compare the vulnerability counts across tags to see whether the vulnerabilities are decreasing or increasing over time.
Fix vulnerabilities
Once a list of vulnerabilities have been identified, there are a couple of actions you can take to remediate the vulnerabilities. For example, you can:
- Specify an updated base image in the Dockerfile, check your application-level dependencies, rebuild the Docker image, and then push the new image to Docker Hub.
- Rebuild the Docker image, run an update command on the OS packages, and push a newer version of image to Docker Hub.
- Edit the Dockerfile to manually remove or update specific libraries that contain vulnerabilities, rebuild the image, and push the new image to Docker Hub
Docker Scout can provide you with concrete and contextual remediation steps for improving image security. For more information, see Docker Scout.
Turn off static vulnerability scanning
Repository owners and administrators can disable static vulnerability scanning on a repository. To disable scanning:
Sign in to Docker Hub.
Select My Hub > Repositories.
A list of your repositories appears.
Select a repository.
The General page for the repository appears.
Select the Settings tab.
Under Image security insight settings, select None.
Select Save.